Tapping into the iPhone onboard accelerometer using "Gyrosc" App and transmitting over OSC to Pure Data...Very strange when you try to film the screen with the phone while moving around, gives the illusion of a hole or mirror in the screen. Hard to explain...
Tag: Technology
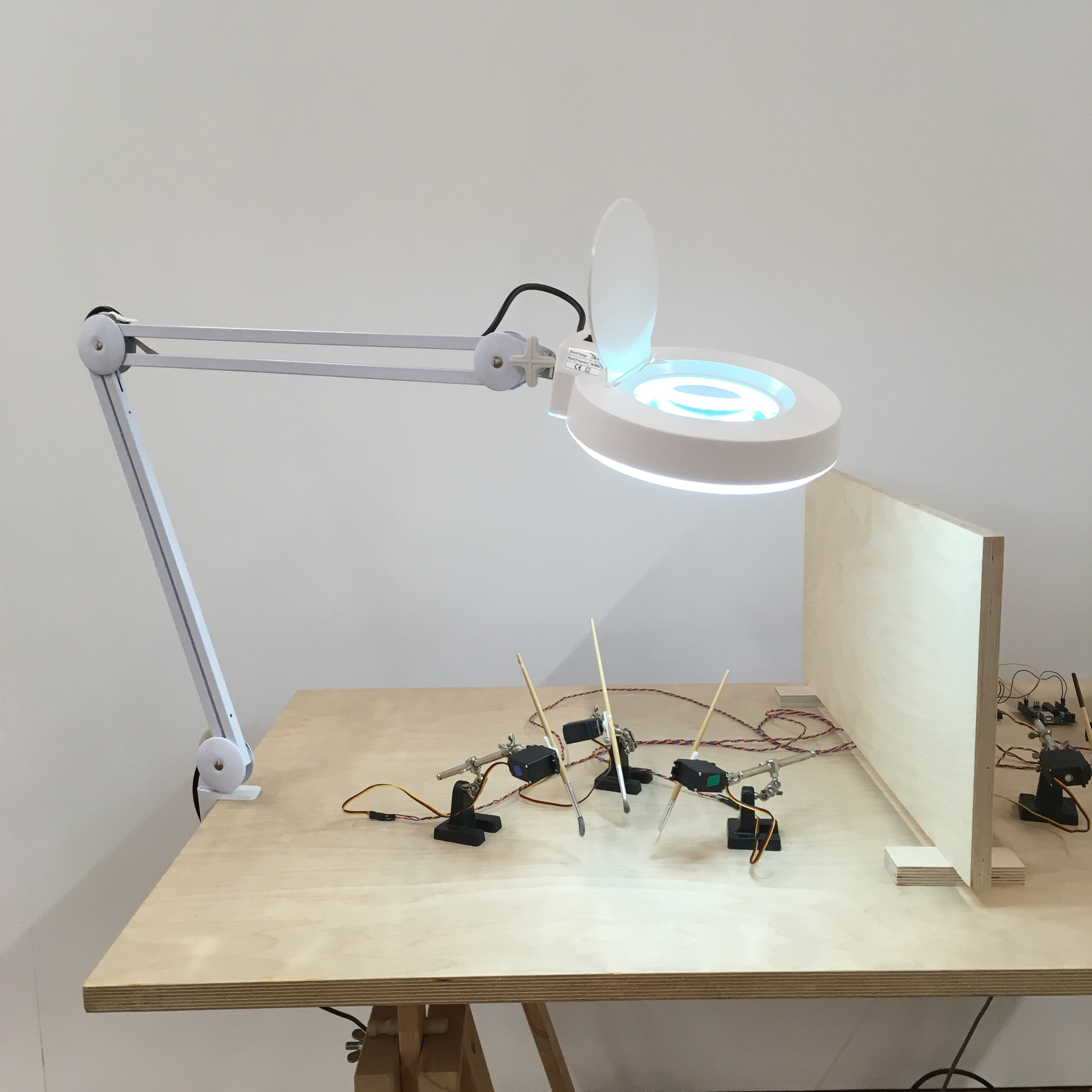
Tactile Anchoring Device [Images]
Augmented hands
‘Augmented hand series’ by Golan Levin, Chris Sugrue, and Kyle McDonald, 2013-2015) ‘MIRAGE Illusion Box’ (Roger Newport, 2008) These are two very similar projects which both transform the image of a hand in real time using Augmented Virtuality (AV, the digital manipulation of real-world objects). Both take the form of a black box, into which the hand is placed. When inside the participant can see their hand as if looking through a window into the box. Inside the box, a system of mirrors and motion tracking is used. An augmented or distorted digital image of the hand is relayed to a screen on the top of the box. Despite the technical similarities, both works stem from entirely different motivations. The ‘MIRAGE Illusion Box’ (Newport, 2018)
Be Another Lab
This International group interdisciplinary group adopt mechanisms employed in the cognitive sciences, such as the work of Mel Slater, and the arts. Their project ‘The Machine to Be Another’ allows anyone to experience a perspective from the body of an-other. The group speak of ‘expanding subjective experience’ and ‘understanding the relationship between identity and empathy from an embodied perspective’ (http://beanotherlab.org/) Using HMDs and live video, they have developed a number of critical applications. Investigating a wide range of issues including gender and disability. The group study the impact this work can have on people’s lives, employing methods of action research and co-creation. Be Another Lab embraces an open source approach. Sharing and developing their project through workshops, making the tools and
Meeting With Sally Linkenauger
Notes from a meeting With Sally Linkenauger Lancaster University Psychology Dept. After discovering Sally's research at the BRnet conference I wanted to experience her experiments, so I asked if I could visit her lab. The VR lab looks like a normal office space, PCs scattered around the outside, and loads of VR tech hanging around. On closer inspection, a network of cameras is installed around the space to enable complex motion capture and augmented reality experiments to be undertaken. There is a treadmill in the corner. In the experiment I tried, a leap motion sensor captures the movements of your real hand, allowing you to articulate a virtual hand. The experiment requires some time to become used to the VR environment. At first,
Phantom Presence
This experiment induces the sensation of a phantom presence in the room. The participant blindfolded is asked to use a stylus to prod an empty space in front of them. Using a tactile feedback system and a robot arm, the participant feels as if they are prodding themselves in the back. As the experiment progresses the system adds a delay to this prodding. At this stage, the participants become freaked out believing that someone else if prodding them... https://youtu.be/GnusbO8QjbE Link to the paper... Neurological and Robot-Controlled Induction of an Apparition https://www.cell.com/current-biology/abstract/S0960-9822(14)01212-3
Augmented senses
In this experiment, they created a simple device [Hearspace App] incorporating a compass and headphones. It "allows users to reliably hear the direction of magnetic North as a stable sound object in external space on a headphone. They found that "long-lasting integration into the perception of self-rotation. Short training with amplified or reduced rotation gain in the magnetic signal can expand or compress the perceived extent of vestibular self-rotation, even with the magnetic signal absent in the test" I was struck by this statement "sensory substitution and augmentation research has aimed to restore sensory functionality from non-invasive afferent signals of artificial sensors...there has been little concrete evidence that truly perceptual experiences have ever been obtained via this approach" Sensory augmentation: integration of an auditory
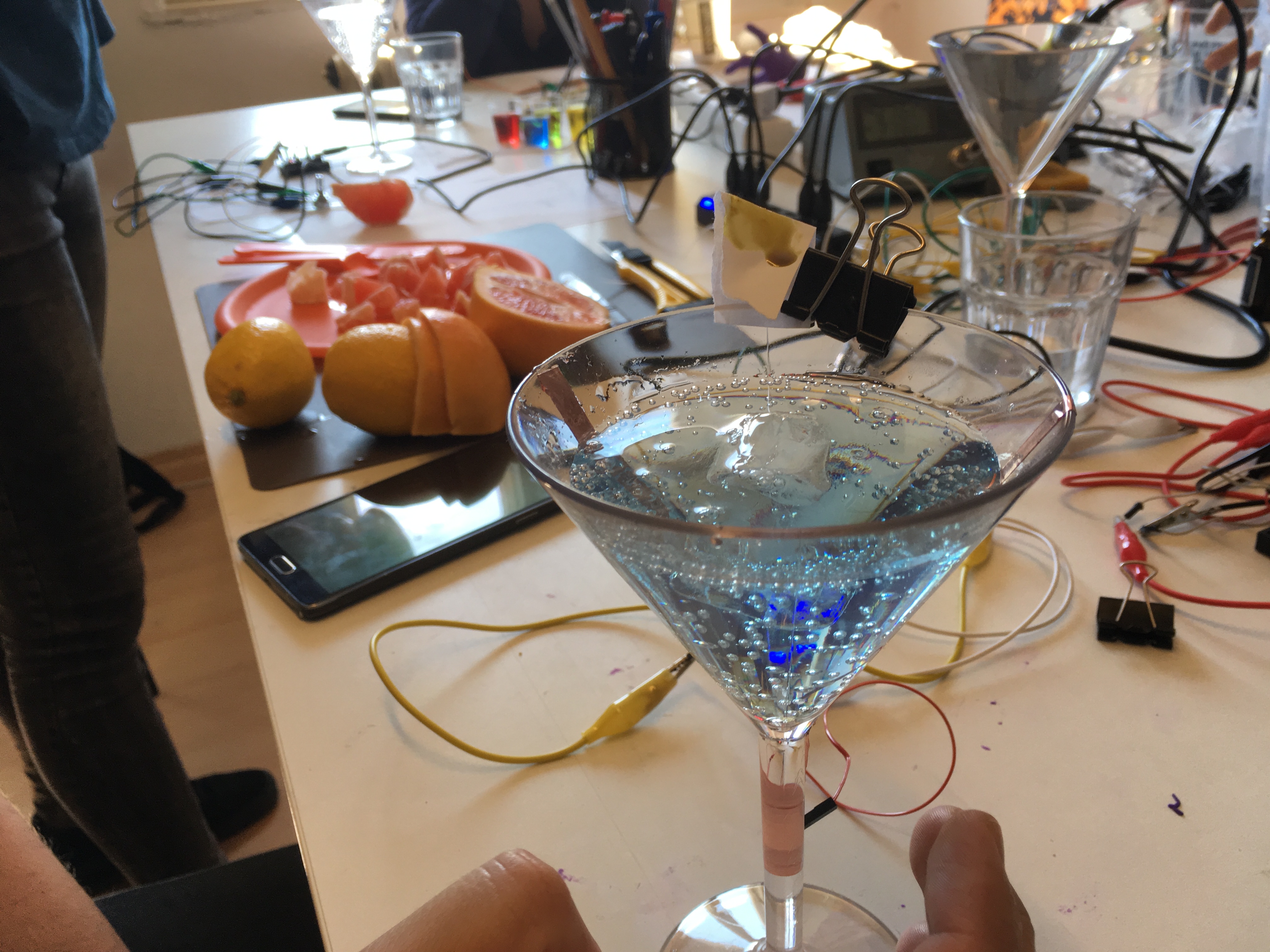
Electronic Taste Perception Workshop – Radiona
[Here is some documentation from one of the activities for the 're-mapping the senses workshop earlier this year...] Our sense of taste is directly affected by the colour and smell of the food. Experiments prove that the colour of a drink affects our perception of its sweetness for example. Altering the sound of the food, say adjusting the high-end frequencies while eating crisps can also affect our perception of the crunchiness of those crisps [see the paper here. Playing with these assumptions and expectations can create heightened food experiences. There have been a number of studies that suggest it is possible to simulate Sweetness, bitterness, sourness. Specifically, we test these settings as claimed by the Vocktail project [see below] to simulate the following sensations... Sour: magnitude of current: 180
Galvanic sensors
Images of my first GSR [Galvanic Skin Response] sensor hacked from a toy lie detector circuit works well but currently looking for better DIY versions to use in experiments. More research on this to be posted soon.
Amplitude Modulation Workshop
I met Martin Howse in 2009 when he invited me to do a workshop for his micro research series in Berlin. At the time he had a fantastic apartment with a large garage space for a studio. The large table at its centre became sprawled with electronics by the end of the day. I had the opportunity to take a look at some of his projects, wonderful hand-drawn circuits burnt and encrusted that looked more like remnants from some other device of unknown function. For this workshop we investigated Amplitude Modulation, turning light into sound, use of the LM chips as an amplifier and using light sensors as an input, and making LEDs and lasers transmit sounds and signals through light