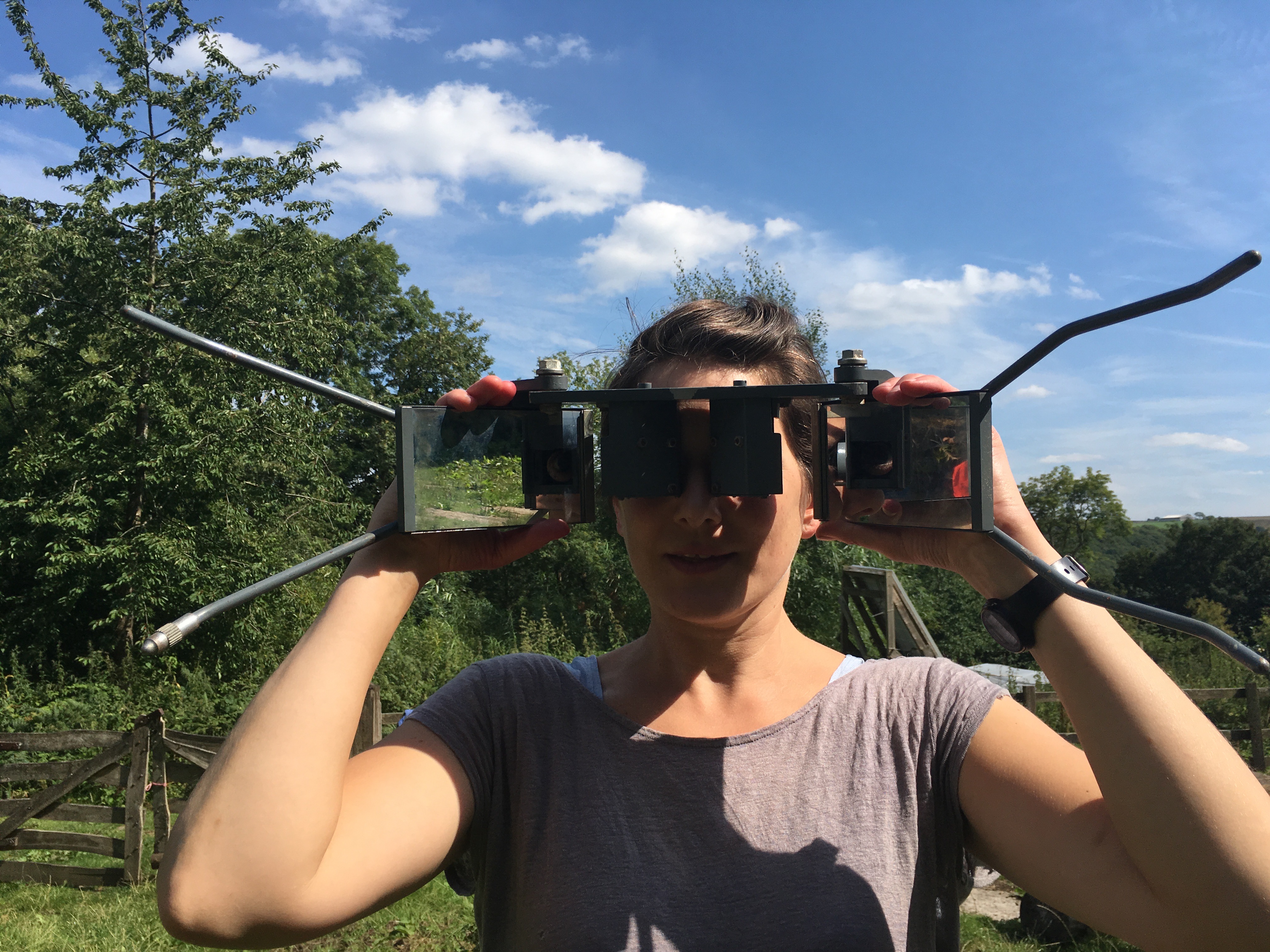
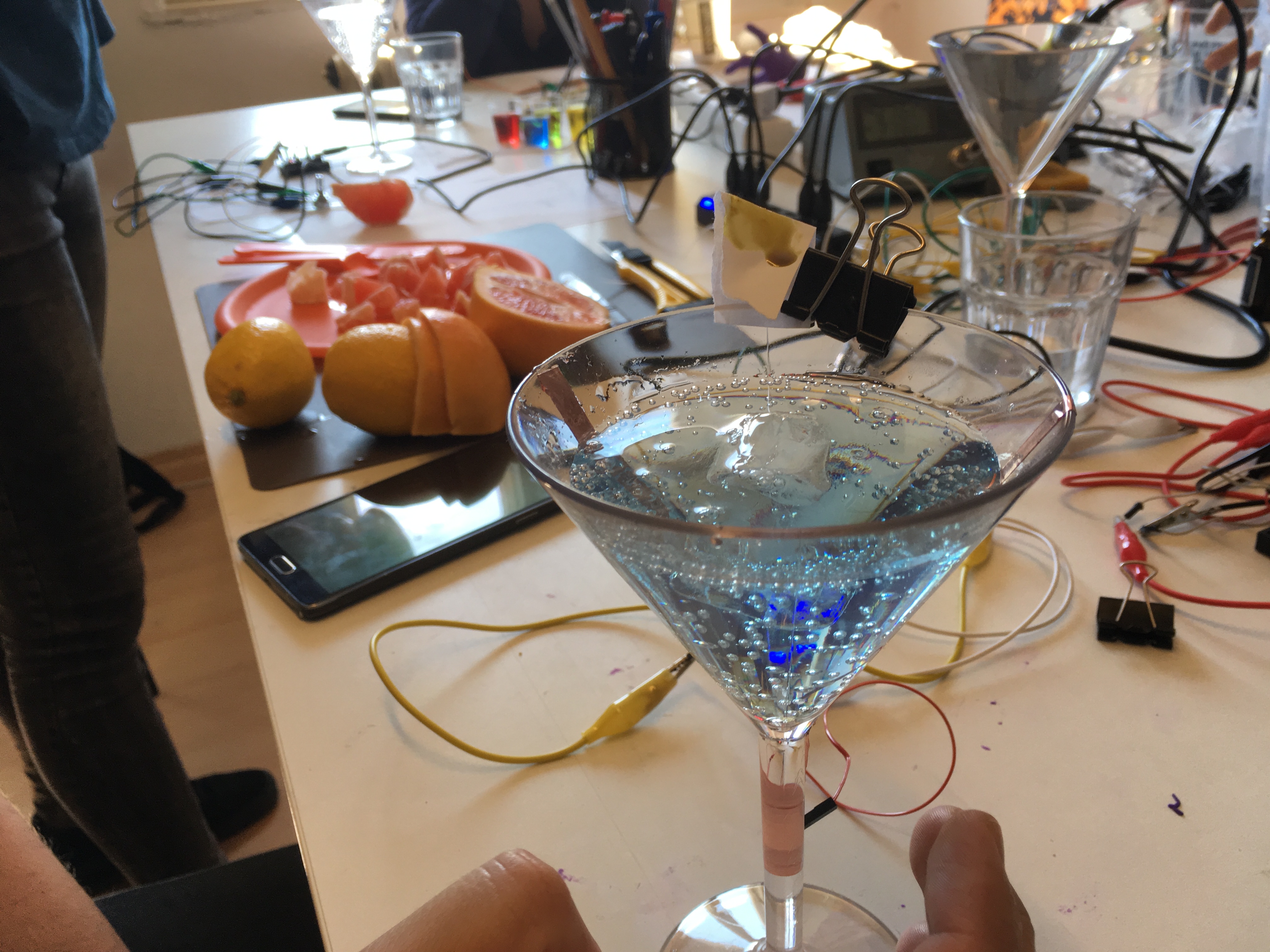
I took part in a study at BEAM LAB as a 'neurotypical control subject. This was my first experience in experimental psychology as a participant. I found this deeply significant for my research; actually experiencing the full process of an experiment in the context of a lab. There were a number of questionnaires and tasks. Psychometric tests are concerned with the measurement of mental abilities, personality traits, intelligence. Typically these will be questionnaires and other puzzles 'tasks'. I found the activity to be deeply relaxing. also the format, in my opinion, ripe for creative subversion. It generated a lot of new ideas which I will write about this experience in more detail soon.
Author: antonyhall
Constructing a sense of self
"He felt dizzy, stood up, turned around, and saw himself still lying in bed. He was aware that the person in bed was him, and was not willing to get up and would thus make himself late for work. Furious at the prone self, the man shouted at it, shook it, and even jumped on it, all to no avail..." This article encapsulates some of the most important ideas, concepts and developments which lead towards the experiments on the simulation of out of body experiences. The article mentions Peter Brugger, Olaf Blanke and Thomas Metzinger, as well as some details of patient experiences, and the story of how this experiment came about. As well as the illusion of seeing one's self"autoscopy' There
Alfons Schilling
"Schilling's work is a discourse on the anatomy of illusion. a return to the physical experience of perception. this work locates the visual experience in the brain by completing its visual text there. The art of Schilling opens up a critical dialogue between the arts. This view of art as a sense experience, as the convergence of the work and the perceiver, which brings the work into existence, establishes the basis of that experience as a means of deconstructing reality and constructing through that experience a path toward a renewal, and the opening up of the perceptual (sense) experience." John G. Hanhardt, Curator of Film and Video, Whitney Museum of American Art, New York 1977. Random Dot stereo works https://www.alfonsschilling.net/werke/randomdot-stereo/ http://www.vasulka.org/archive/Artists6/Schilling,Alphons/SchillingPoster2.pdf http://www.vasulka.org/archive/Artists6/Schilling,Alphons/ElectronicSpaces,etc.pdf An article discussing the
Rubber/clay Hand experiment UoM
I supported some seminars on the Rubber Hand Experiment with undergraduate psychology students, presenting some of my research ideas [unfeasable objects and the Clay Hand Experiment] The idea was they experience the experiment for themselves before designing their own.
Fieldwork under the ‘Darkest sky’
I was invited by Annie Carpenter and Nicola Ellis to Allenhead Arts for a few days of art and science during the night of the Orionids meteor shower, hoping for clear yet dark skies. They had been resident artists there over the last few months https://www.acart.org.uk/ . In a continuing effort to make my activities more sustainable and portable, I decided to cycle from Penrith to a remote location in the heart of the North Pennines which boasts the darkest skies in the UK. I was one of the most hellish bike rides I have ever endured. And I am no stranger to big hilly bike rides. One of my typical problems when taking part in this kind of open-ended participatory creative
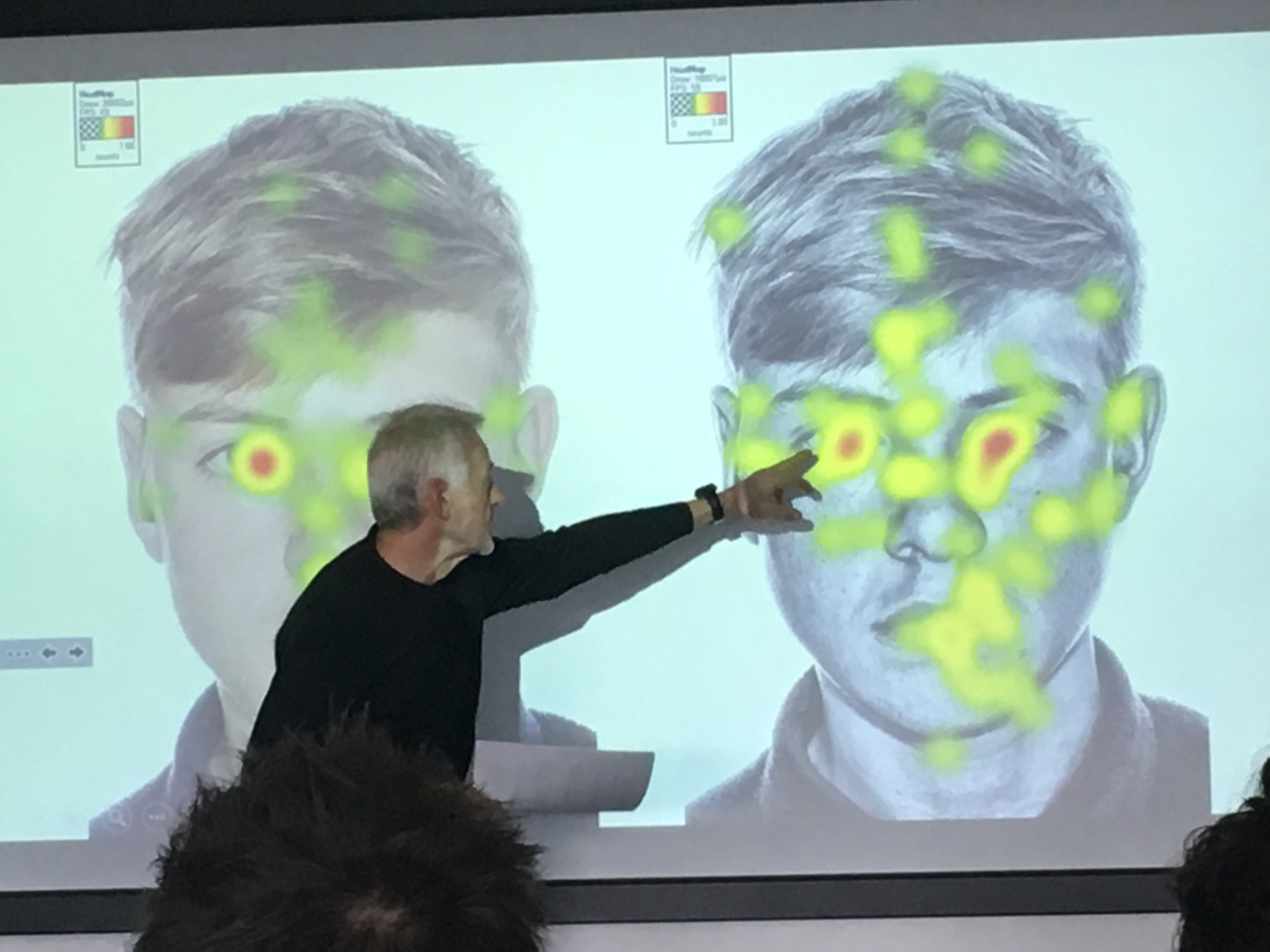
Eye tracking experiment planning
Inspired by last weeks conference and some examples of how artists are working with Eye Tracking, I went back to BEAM Lab the following week to start the process of learning how to set up my own experiment using Eye-tracking. My plan is to incorporate this with the strange face in the mirror experiment. My main problem is how do I calibrate the sensor - if I am to measure how they look at a reflection how do I map this precisely to the sensors. Normally the experiment has the participant looking directly at a screen surface, but how would this work with a reflected image? So I need to get a two-way mirror and perhaps get the participants to draw the
Eye tracking in arts research
Notes from the Digital Humanities, Human Technologies / AHRC NWCDTP Postgraduate Conference 2018 / part 1 https://nwcdtpconference2018.wordpress.com/home/ John Merrill [MMU] presented his project; Portrait as Landscape: Rendering the Unseen surface of the face. He explained some ideas behind visual perception and the evolution of the eye, and its flaws which were a great introduction to the project. Merrill creates digitally processed high contrast, large-scale photographs. Sharpening and enhancing the surface topography and textures of the face. The idea is that attention is taken away from thinking about the character of the person pictured, and moving away from the stereotypes associated with how we recognise faces and make judgments about character. The idea is that we are left to think about the more
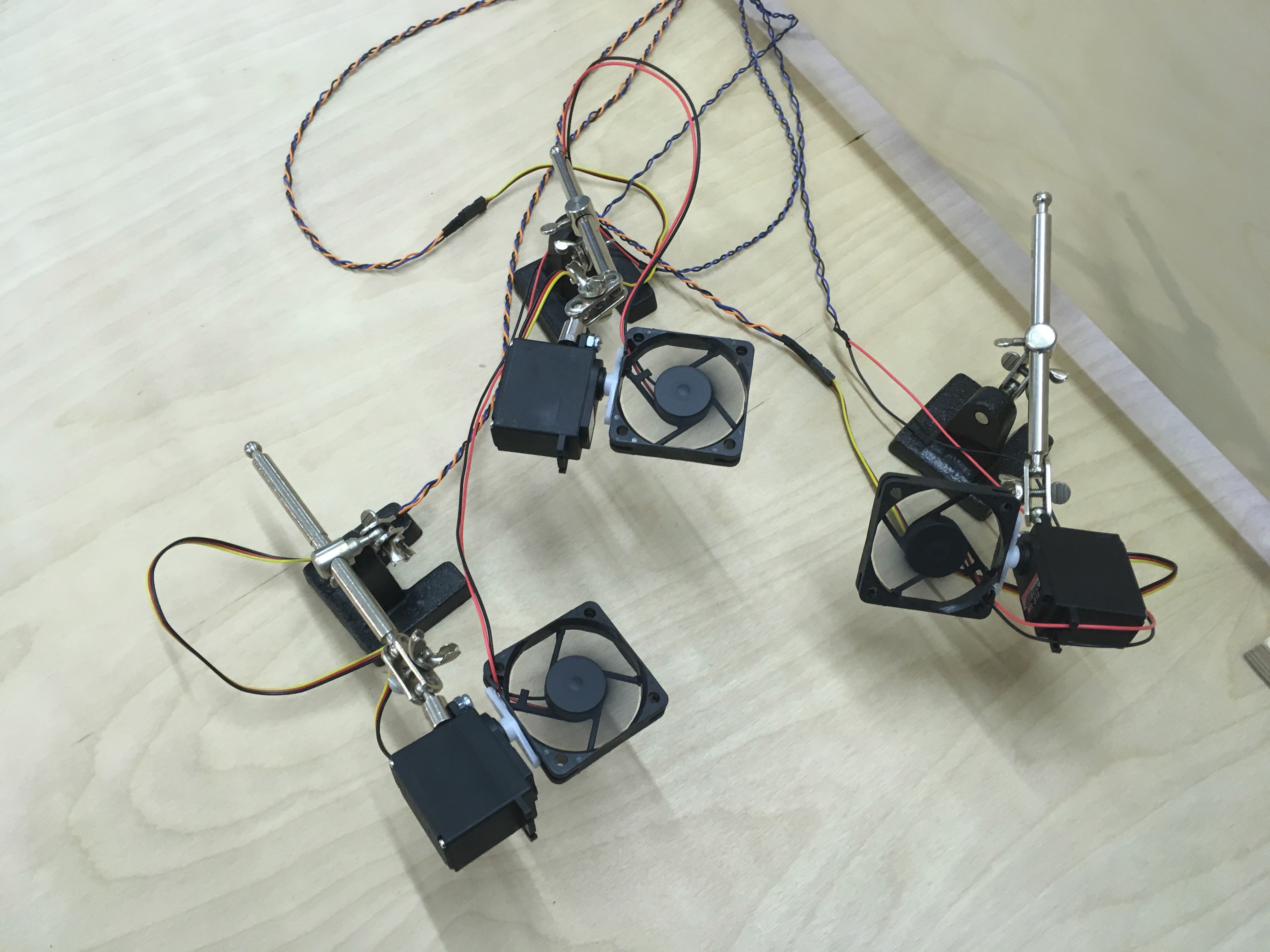
Tactile Anchoring Device [Images]
Carsten Holler / Olafur Eliasson
Carsten Holler is a key example within this study, often re- appropriating science for the purposes of art. Staging ‘Quasi-scientific’ experiments (Windsor, 2018) which transform the gallery into a laboratory. Often disorientating the viewer, or more appropriately, the participant. As well as the large-scale installations smaller performative works such as ‘Kit for Exploration of the Self’ (Carsten. Holler, 1995) take the form of durational perception changing instruments such as ‘Upside Down Glasses’ (Carsten Holler, 1994-2018). These both directly re-appropriate methods from experimental psychology (Stratton, 1896). Many of the works require the participant to travel through them or offer the opportunity to make decisions of which there are no return or unknown outcomes, further reinforcing this active notion of experience as
Augmented hands
‘Augmented hand series’ by Golan Levin, Chris Sugrue, and Kyle McDonald, 2013-2015) ‘MIRAGE Illusion Box’ (Roger Newport, 2008) These are two very similar projects which both transform the image of a hand in real time using Augmented Virtuality (AV, the digital manipulation of real-world objects). Both take the form of a black box, into which the hand is placed. When inside the participant can see their hand as if looking through a window into the box. Inside the box, a system of mirrors and motion tracking is used. An augmented or distorted digital image of the hand is relayed to a screen on the top of the box. Despite the technical similarities, both works stem from entirely different motivations. The ‘MIRAGE Illusion Box’ (Newport, 2018)
Be Another Lab
This International group interdisciplinary group adopt mechanisms employed in the cognitive sciences, such as the work of Mel Slater, and the arts. Their project ‘The Machine to Be Another’ allows anyone to experience a perspective from the body of an-other. The group speak of ‘expanding subjective experience’ and ‘understanding the relationship between identity and empathy from an embodied perspective’ (http://beanotherlab.org/) Using HMDs and live video, they have developed a number of critical applications. Investigating a wide range of issues including gender and disability. The group study the impact this work can have on people’s lives, employing methods of action research and co-creation. Be Another Lab embraces an open source approach. Sharing and developing their project through workshops, making the tools and
Labyrinth Psychotica
Labyrinth Psychotica is an artistic research project that aims to simulate the experience of psychosis. It uses multisensory [tactile and sonic] elements in combination with the maze environment, to create a fully immersive experience. The maze mechanism also serves as a metaphor for attempting to get inside the mind of another. The investigation aimed to not only portray an experience of psychosis but one that was ‘artistic’. It further asks if such an endeavour could prove ‘useful’. Though I can only speak from my experience of the work [1], it did seem effective in conveying elements of this experience, such as; loss of personal boundaries, and blurred borders between the body and space. Another element which resonates with Action Lab is the
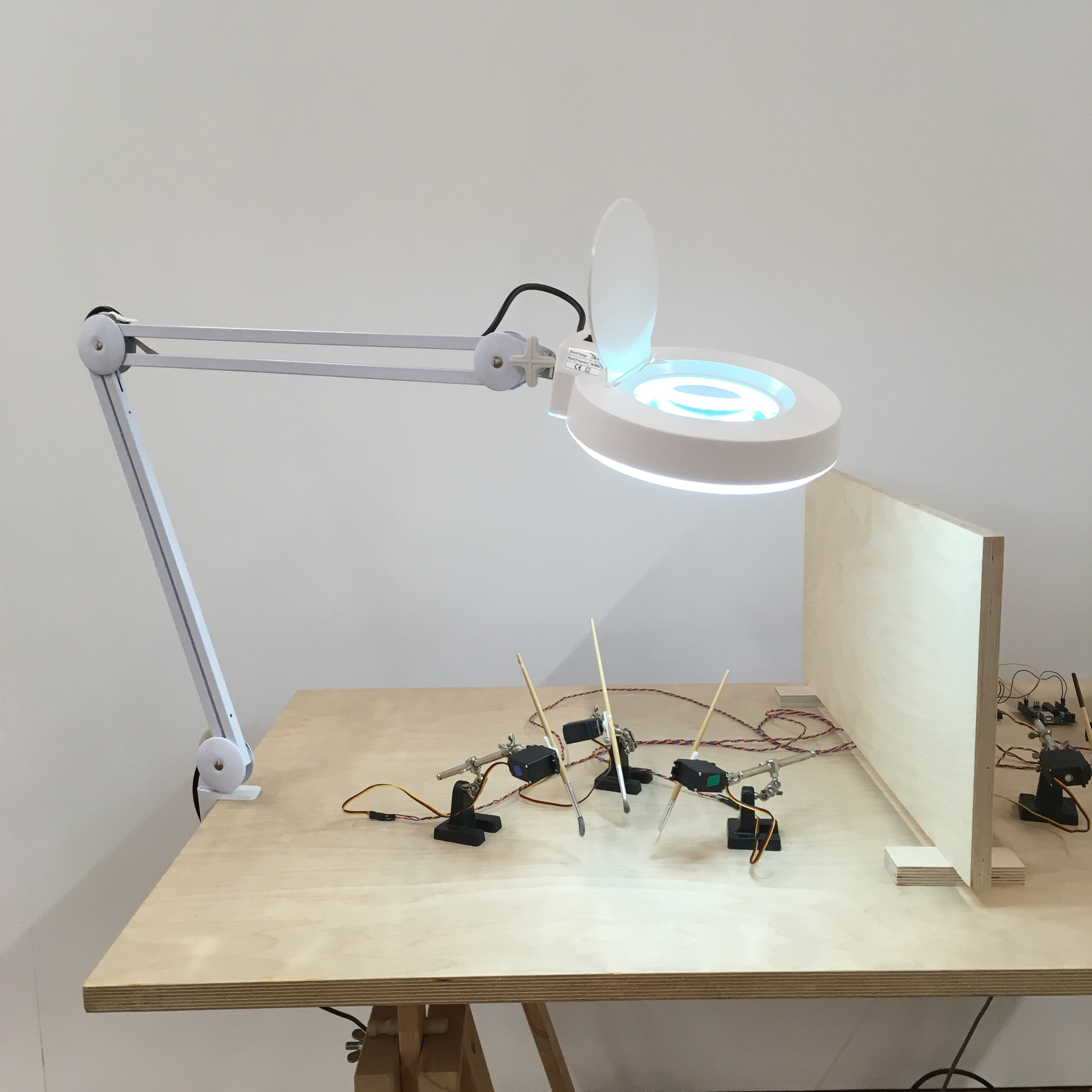
Tactile Anchoring Device prototype 2
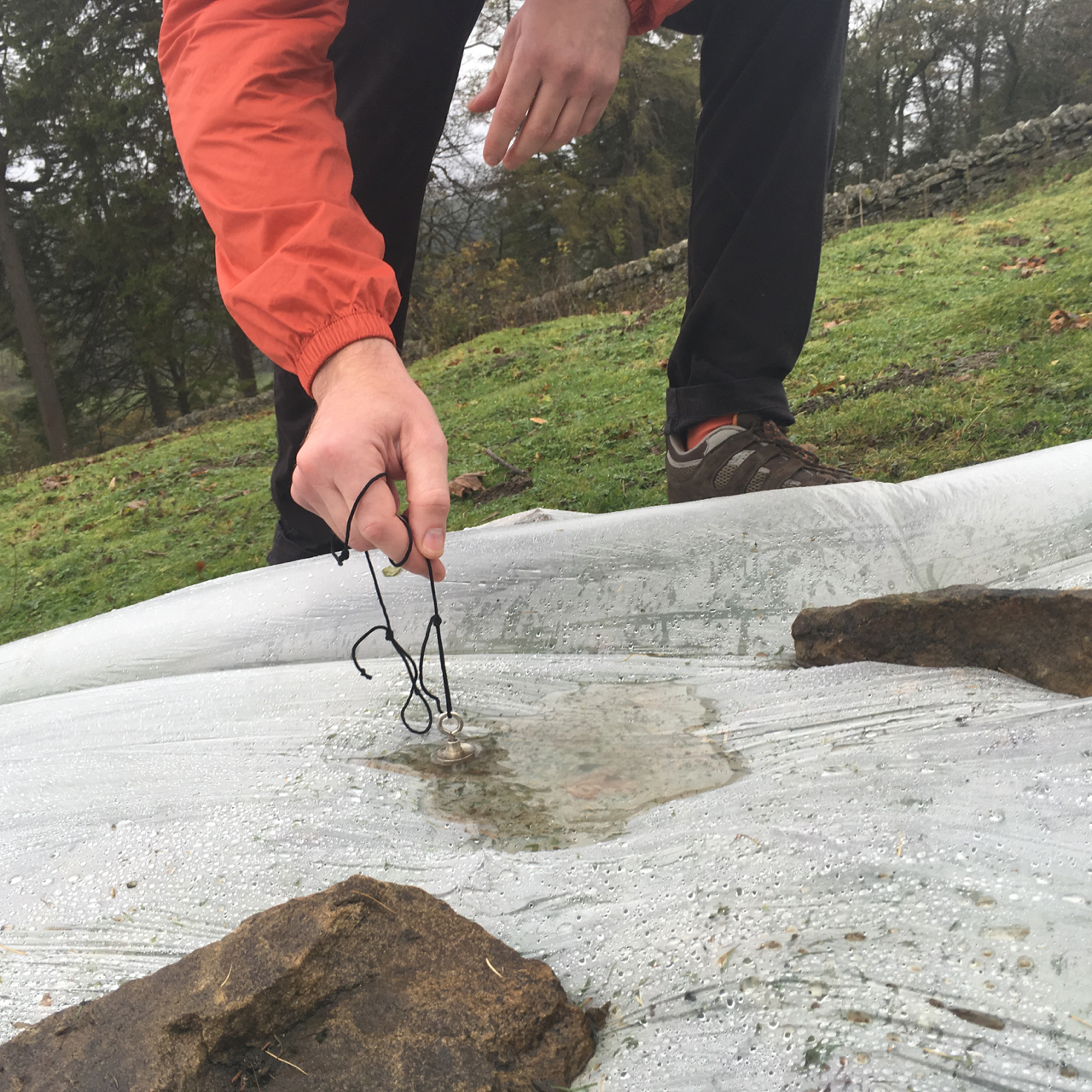
The first film of the Tactile Anchoring Device in progress, showing the use of brushes and fans to generate the illusion of an invisible hand... https://youtu.be/vHaB6HBbQrs The system is based on an Arduino controls two sets of identical stimuli which move in synchronisation with each other [ servo motor, articulating solenoids, fans, lamps etc] Once the participant is experiencing the illusion, the operator or autonomous systems can trigger a ‘shock’ or threat stimuli. This is currently in the form of a solenoid which releases a heaved plum line weight which drops into the empty space. See the project page here. http://antonyhall.net/blogtactile-anchoring-device/
Meeting With Sally Linkenauger
Notes from a meeting With Sally Linkenauger Lancaster University Psychology Dept. After discovering Sally's research at the BRnet conference I wanted to experience her experiments, so I asked if I could visit her lab. The VR lab looks like a normal office space, PCs scattered around the outside, and loads of VR tech hanging around. On closer inspection, a network of cameras is installed around the space to enable complex motion capture and augmented reality experiments to be undertaken. There is a treadmill in the corner. In the experiment I tried, a leap motion sensor captures the movements of your real hand, allowing you to articulate a virtual hand. The experiment requires some time to become used to the VR environment. At first,
Seeing with the tongue – Paul Bach-y-Rita –
"You don't see with the eyes. You see with the brain" Paul Bach-y-Rita, Science News Online 1 Sept, 2001; vol. 169, no. 9 Paul Bach-y-Rita was one of the first neuroscientists to study the idea of Neuroplasticity. He did a number of experiments on sensory substitution, developed the idea of "Brain Port" in 1998. This interface uses a camera to feed an image to an electrode array placed on the tongue. Blind patients were able to see using the tongue. And a chair, the back of which is packed with solenoids, the camera feeds an image to these. After time and with training the user is able to sense images, at first basic shapes, and with more time can sense more detail such
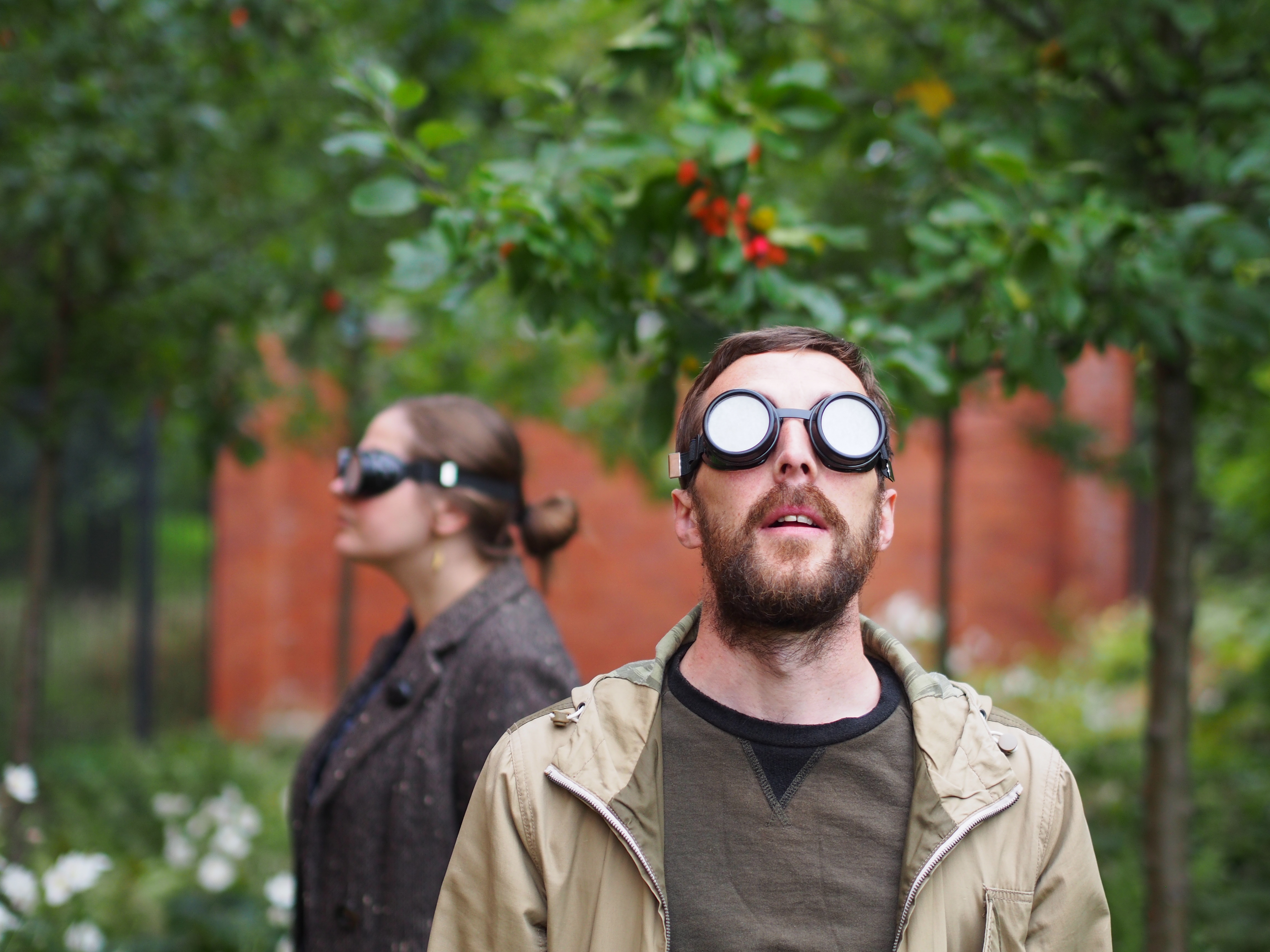
Aperture navigation
From the field research trip to the Middlewood Trust, I developed a set of goggles with a small hole and slot apertures. Participants report different perceptions of time and space, and of sound and distances. I thought I had walked for a great distance, only to find I had only moved a few meters. One participant spoke of having 'microscope eyes' and how 'the closer you get to things, the less you can see of them' focussing and depth of field also become more apparent. Here is the extract from my experience: "Seeing through the small aperture also had the effect of making things seem like an old movie [grainy and soft-edged]. After wearing these for a while, I could hear others
Navigations
The Ganzfeld [ 'total field' ] experiment is a form of perceptual deprivation, giving an experience of a uniform field of light [More information here] . has become a staple activity in my workshops. Rather than sitting still and listening to sounds I have been opening this up as a mobile activity, or 'navigation' as I have started to call it. It serves as an icebreaker, often requiring people to work in pairs to move through spaces, following ropes or sonic stimuli. The purpose is to heighten the participant's awareness through altering their perceptual experience of space. Participants become aware of new structures of light or start using the body in a different way in order to move, becoming more
Lenticular goggles
Speaking with an artist while making plans for a future Action Lab, I came up with the idea of making these lenticular glasses [Above], which use a lenticular lens [textured with lines or ridges] which have the effect of dividing the visual field into lines. In an urban or interior space, vertical and horizontal lines are common. These become enhance or reduced depending on the orientation of the lens. Using the lens in a vertical alignment, steps become invisible, but when the lens is rotated they become enhanced. Using a combination of both things get even stranger. Point light sources create strong bright lines. I have yet these in a natural environment.
The Multi-faceted body
A few notes from the BRnet Conference the Multi-faceted body. June 2018, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK I felt strangely at home among so many research projects that use the hand as a model for the wider issues of body representation and ownership. Keynote speaker Mel Slater's talked about his playful and engaging research. Slater’s work centres around the idea of using immersive virtual reality as a medium to transform the self, not just the reality of a space. His research projects include self-help therapy. The project Personified Self Interaction (Osimo et al., 2015) allowed ‘you’ [embodied within an avatar of Freud] are able to talk to ‘yourself’ [an automated replay of you, embodied within an avatar of yourself] and vice-versa. This enables the
Phantom Presence
This experiment induces the sensation of a phantom presence in the room. The participant blindfolded is asked to use a stylus to prod an empty space in front of them. Using a tactile feedback system and a robot arm, the participant feels as if they are prodding themselves in the back. As the experiment progresses the system adds a delay to this prodding. At this stage, the participants become freaked out believing that someone else if prodding them... https://youtu.be/GnusbO8QjbE Link to the paper... Neurological and Robot-Controlled Induction of an Apparition https://www.cell.com/current-biology/abstract/S0960-9822(14)01212-3
Fieldwork / Night walk
I teamed up with artist Annie Carpenter to pull together a small group of artists and friends for a night of ‘fieldwork’. We organised an overnighter to do some experiments and have discussions together in the relaxed atmosphere of Middlewood Trust study centre; an off-grid permaculture farm. I had worked here before with [Annie and Sam Illingworth] doing some workshops with their students on a previous 'field research' style project. The concept captured my interest. We wanted to create a situation where we could work as well as have time and space to chat about ideas with others. My equipment consisted of my laptop, Arduino, [with a relay shield for experiments] and some electronics, GoPro, 360-degree camera. Also a heavy rechargeable
Tactile Anchoring Device Prototype 1
Here is my prototype device intended to help autonomously generate the 'invisible hand illusion'. For this experiment, I created a series of brushes which rotate at different speeds stroking empty space. The idea was that the participant watches this device, while the brushing motion is replicated one their real hand hidden nearby. This is building towards a piece of work called 'On the embodiment of a discrete Volume of Empty Space' [ See http://antonyhall.net/blogtactile-anchoring-device/ ] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DI-f6KgRD2w&w=700&h=400
Augmented senses
In this experiment, they created a simple device [Hearspace App] incorporating a compass and headphones. It "allows users to reliably hear the direction of magnetic North as a stable sound object in external space on a headphone. They found that "long-lasting integration into the perception of self-rotation. Short training with amplified or reduced rotation gain in the magnetic signal can expand or compress the perceived extent of vestibular self-rotation, even with the magnetic signal absent in the test" I was struck by this statement "sensory substitution and augmentation research has aimed to restore sensory functionality from non-invasive afferent signals of artificial sensors...there has been little concrete evidence that truly perceptual experiences have ever been obtained via this approach" Sensory augmentation: integration of an auditory
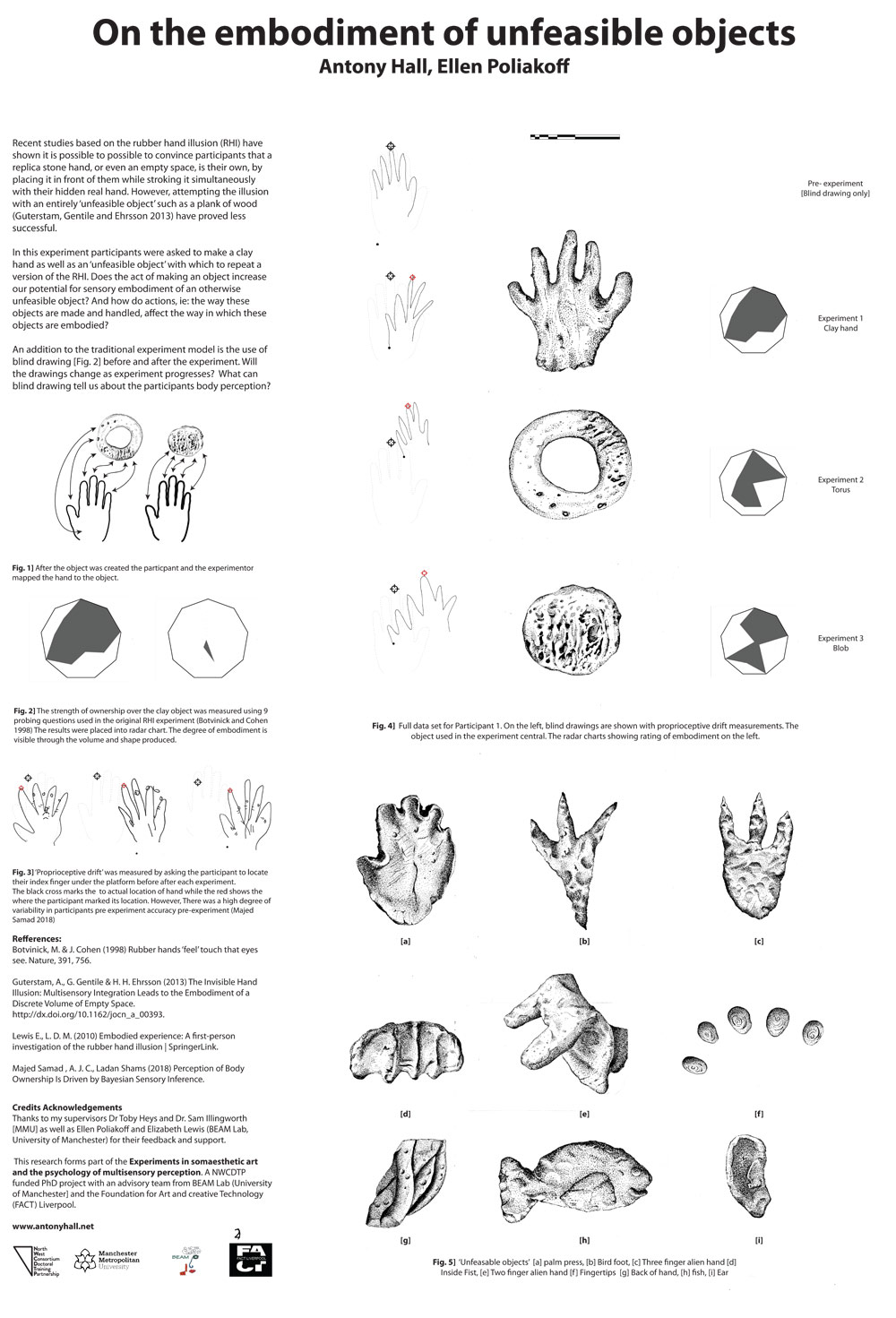
“On the embodiment of a discrete volume of empty space”
As I mentioned before [Illusions of Invisible, alien hands, 3 arms, and shrinking bodies…] The Invisible Hand Illusion is a version of the Rubber hand illusion which uses no fake rubber hand at all. Instead, the participant focuses on an empty space in place of their hand. Sometimes a handless stump, and as a control, a wooden plank. they found that participants could embody a ‘Discrete Volume of Empty Space’. This interests me as it fits with a number of works which challenge the physicality of the art object, instead, I have presented amorphous forms of bubbling materials or even a plinth which automatically concealed the object. The idea of making an automated system to generate the illusion of an invisible hand seems the next step for my research.
Simulation of touch
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKMndCEr4Mw
Poster – BRnet Conference 2018
Electronic Taste Perception Workshop – Radiona
[Here is some documentation from one of the activities for the 're-mapping the senses workshop earlier this year...] Our sense of taste is directly affected by the colour and smell of the food. Experiments prove that the colour of a drink affects our perception of its sweetness for example. Altering the sound of the food, say adjusting the high-end frequencies while eating crisps can also affect our perception of the crunchiness of those crisps [see the paper here. Playing with these assumptions and expectations can create heightened food experiences. There have been a number of studies that suggest it is possible to simulate Sweetness, bitterness, sourness. Specifically, we test these settings as claimed by the Vocktail project [see below] to simulate the following sensations... Sour: magnitude of current: 180
Making Immersive Experiences
“ What do new immersive technologies, such as augmented reality, virtual reality and artificial intelligence, offer storytellers and makers? And do they change the stories we choose to tell audiences? Two internationally renowned digital storytellers and makers present their latest creative projects and help us to find answers to these questions.” Notes from 'Making Immersive Experiences 1: Lance Weiler, Storytelling Lab, Columbia University + Chris Mullany, Marshmallow Laser Feast' Organised by Immersion Research Group, Manchester Metropolitan University Immersive storytelling is not something I have really ever thought about in relation to my work, however, I find the ideas discussed resonated strongly with my own practice and collaborations I have been part of. While listening to the speakers I realised I have taken part in
VR technology
Some notes and links, reflecting on the VR mask. The absurdity of the interface is both clumsy and undignified technology orientated experience.... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtwZXGprxag The Sword of Damocles 1968 was the first HMD unit, invented by Ivan Sutherland. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gWLHIusLWOc "The intention of Birdly® is to fulfil people’s ancient dream of flying. With virtual reality (VR) and robotics technology, SOMNIACS creates an extremely vivid full-body experience that makes you instantly forget the mechanics and computer codes behind this spectacular apparatus. The immersive and interactive nature of Birdly® serves one goal: to enjoy the ultimate freedom of a bird and intuitively explore the skies." http://www.somniacs.co/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qh2UdRKNqH4
Experimental Psychology Lab
I have been considering what an Experimental Psychology lab looks like. What objects might these contain? Typically these consist of office like rooms, chairs and tables, perhaps an observation room. These days a computer, sensors for eye tracking and biometric measurement would be commonplace. Headphones, and VR equipment. EEG and MRI image may also be used in more advanced studies. Ultimately Experimental Psychology is an interdisciplinary subject and experiments could cross over to neurosciences, AI and robotics. But a google search of Experimental Psychology laboratory yields some interesting results. I'd be interested to know what other instruments and devices I should look at when thinking about this field of research. Please let me know if you know what any of these items might